
It can be considered as an extension of the valence bond concept and lays its foundation on the molecular and quantum mechanics of an atom. The concept of Hybridization decrees that atomic orbits fuse with one another to form new degenerated hybrid orbitals, which influence bonding properties and molecular geometry of the atoms of an element. While this makes the molecule symmetrical, it also makes it a non-polar molecule, as the bond polarity of each Nitrogen-Hydrogen bond cancels out.įor better understanding, you can also refer to the already written article on the polarity of NH4.īelow is the image of the geometrical representation of the NH4+ molecule. Since NH4+ is a cation, the bond angle between 2 respective hydrogen atoms is 109.5 degrees instead of 90 degrees, which is as far away from one another as possible.Ī smart way to remember the structure of ammonium is that ‘tetra’ stands for four, that is the number of bond pairs nitrogen makes in Ammonia. This means that NH4+ has 4 pairs in total, which are bonded due to the 4 atoms of hydrogen. Nitrogen, having 5 valence shell electrons, along with 4 from Hydrogen, should have had 9 electrons.īut the + sign decrees that NH4+ has 8 valence shell electrons, due to the positive ion. The 3-dimensional geometrical structure of ammonium, NH4+ is referred to as Tetrahedral. One can draw the 3-dimensional structure of an atom once they have the Lewis Structure of an atom. The properties of an atom identified through molecular geometry help in understanding the behavior, utility, and reactivity of the element.ĭepending upon their geometry, various molecular structures can be classified into linear, angular, trigonal planar, octahedral, trigonal pyramidal, among others. Molecular geometry also helps to determine the atomic properties of an element, such as polarity, magnetism, reactivity, color, biological potency, and 3-dimensional space alignment. The concept of molecular geometry aims to depict the generic shape and structure of a molecule, accurate to the length between different bonds, the bond and torsional angles, other geometrical factors and variables that govern the shape and arrangement of an atom, and therefore, a molecule. While the Lewis Structure is a 2-dimensional depiction of an atom of a molecule, molecular geometry is the visualization and designing of the atoms in a 3-dimensional space. The loss of an electron is depicted by putting a + sign enclosing the Lewis structure.
#Ph3 molecular geometry full
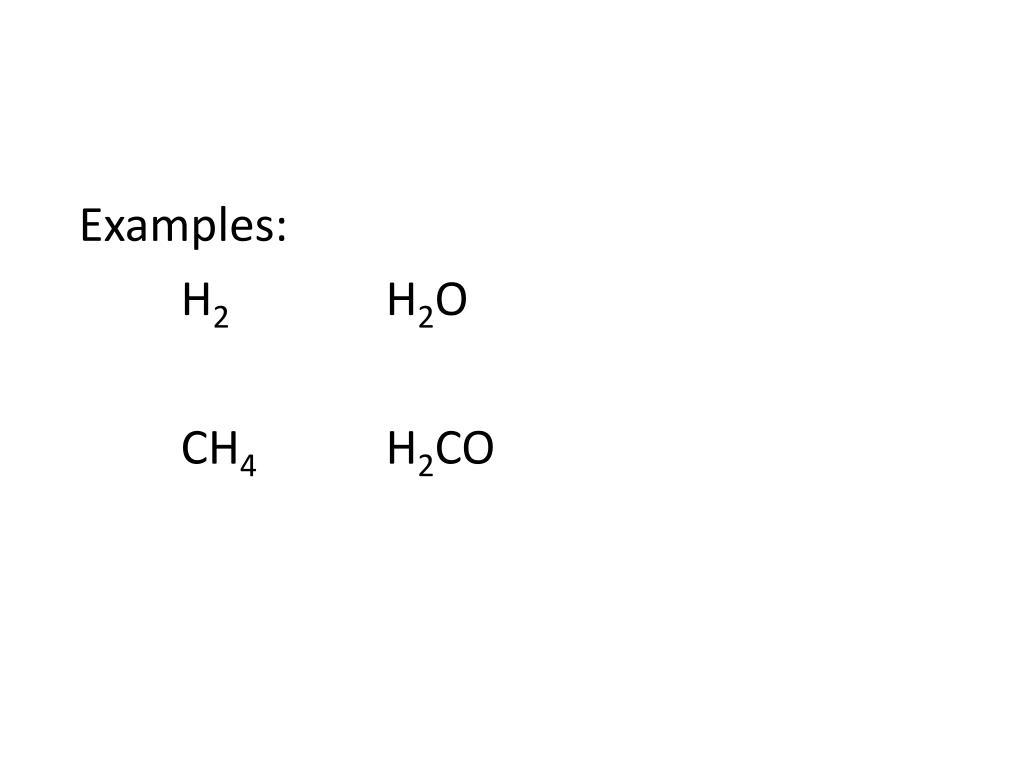
Even Nitrogen, which needs 8 electrons in the valence shell has all 8 of them, thereby forming a full exterior shell. Referring to the octet rule, hydrogen needs only 2 valence electrons, which it already has. Since the NH4+ atom has 8 valence electrons, our arrangement will be according to 2,4,6, and 8.

Keeping Nitrogen in the center, and considering Hydrogen’s position on the outside, we can place the 4 hydrogen atoms surrounding the single nitrogen atom. If we total out the number of electrons, it will be (1×4) + (5×1) – 1 = 4 + 5 – 1 = 8.
#Ph3 molecular geometry plus
The plus sign denotes the absence of 1 electron therefore, it is minus one.

Nitrogen’s valence electron count, however, is 5, owing to its position in the 5th group of the periodic table.

NH4+ has 4 hydrogen atoms, therefore, there are 4 hydrogen electrons. If we look towards the periodic table, we will find Hydrogen in group 1. While understanding the concept of Lewis Structure, it is essential to keep in mind that the idea is neither to explain the molecular geometry nor of the formation of bonds nor of the electron sharing between two atoms of one or multiple elements.Īs mentioned earlier, NH4+ is made up of Nitrogen and Hydrogen. The end goal is to identify a configuration with the best electron arrangement such that the formal charges and the octet rule are upheld. In the Lewis Structure, electrons are depicted as dots.Ī bond between two electrons is represented by a line marked by a dot at both ends, involving the participating electrons. Lewis Structure is a simplified arrangement and presentation of the electrons present in the valence shell of a molecule.Ī Lewis Structure is a depiction of the arrangement of electrons in the standalone atoms of an element.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
